Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is a dynamic and ever-evolving financial market that impacts our daily lives in countless ways. From the cost of your morning coffee to the price of a plane ticket, forex plays a pivotal role in the global economy. In this guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of forex trading, covering essential concepts, terminology, and strategies to help you navigate this vast market with confidence. Let’s get started!
What Is Forex Trading?
Forex, short for foreign exchange, refers to the global marketplace for trading currencies. Unlike traditional markets that deal in goods or services, the Forex market revolves around the buying and selling of currencies on the global market. It is the largest and most liquid financial market globally boasting an average daily trading volume of $6.5 trillion far surpassing the stock market, which operates in the billions.
The Forex market operates five days a week, 24 hours a day, starting at 10:00 PM on Sunday and closing at 10:00 PM on Friday. It is a global marketplace where businesses, investors, governments, banks, and retail traders, like yourself, exchange and speculate on currency values. These transactions are facilitated through online brokers, traders uses fundamental and technical analysis to predict the next move of currency pairs whether they will rise or fall.
Currencies in the Forex market are always traded in pairs, such as Euro/US Dollar (EUR/USD) or US Dollar/Canadian Dollar (USD/CAD). This pairing system allows traders anywhere in the world to profit from accurately predicting the direction of price movements. The Forex market holds the title of being the largest.
Major Forex trading hubs are spread across key financial centers, including London, New York, Zurich, Frankfurt, Hong Kong, Singapore, Paris, and Sydney. Once you familiarize yourself with a specific currency pair and conduct thorough research to identify a favorable position, you can maintain that position around the clock if desired. This round-the-clock trading potential provides opportunities to generate substantial profits in less time compared to trading stocks, making Forex an attractive option for many traders.
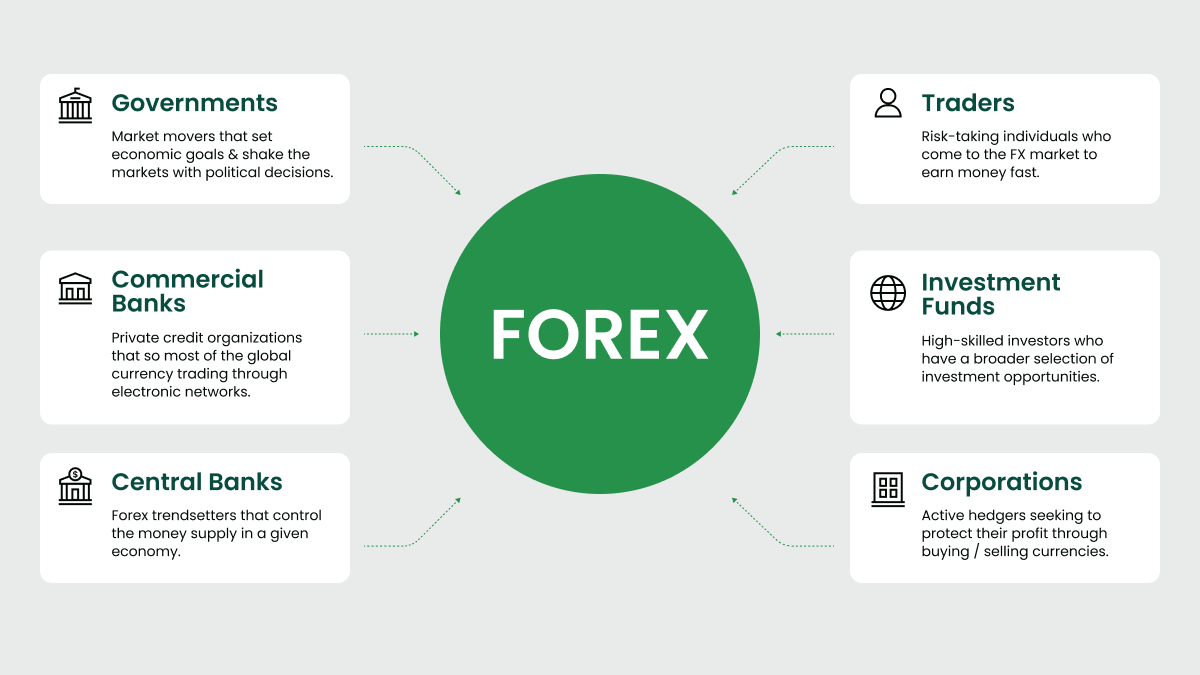
Key Features of the Forex Market
The forex market, often referred to as the foreign exchange market, is a dynamic and highly influential global financial market. Here are the key features that make it unique and appealing to traders worldwide:
1. 24/5 Market Accessibility
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, starting at 10:00 PM on Sunday and closing at 10:00 PM on Friday. This continuous operation ensures that traders can participate at any time, regardless of their location, making it highly accessible to a global audience.
2. Unmatched Liquidity
With a staggering average daily trading volume of over $6 trillion, the forex market is the most liquid financial market in the world. This liquidity ensures that trades are executed quickly, with minimal price fluctuations caused by individual transactions.
3. Global Market Presence
The forex market operates across major financial hubs, including London, New York, Tokyo, Hong Kong, and Sydney. These centers work together in a decentralized structure, ensuring continuous trading activity as the markets in different time zones overlap.
4. Currency Pairs Trading
Forex trading involves trading currency pairs, such as EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar) or USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen). This unique system allows traders to speculate on the relative strength of one currency against another, creating numerous opportunities for profit.
5. Leverage Opportunities
Forex brokers offer leverage, which enables traders to control larger positions with a smaller initial investment. While leverage can magnify profits, it also increases the potential for losses, making risk management crucial.
6. Low Entry Barriers
Unlike other financial markets, forex trading has relatively low entry requirements. With small initial deposits, even retail traders can access the market and begin trading.
7. High Volatility
Price movements in the forex market can be influenced by a variety of factors, including geopolitical events, economic data releases, and central bank policies. This volatility creates opportunities for traders to profit from both rising and falling markets.
8. Diverse Trading Strategies
Forex traders employ a wide range of strategies, including technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and algorithmic trading. The availability of these approaches allows traders to find methods that align with their preferences and goals.
9. Minimal Transaction Costs
Forex trading typically involves low transaction costs, as brokers often charge tight spreads instead of commissions. This cost-efficiency makes forex trading appealing to both beginners and experienced traders.
10. Decentralized Nature
Unlike centralized stock exchanges, the forex market operates through a network of banks, brokers, dealers, and governments. It has no central governing authority.
The unique features of the forex market make it an attractive option for traders seeking flexibility, liquidity, and opportunities to diversify their investment portfolios. However, it’s important to approach forex trading with a solid understanding of its dynamics and a well-defined risk management strategy.
Understanding Forex Basics
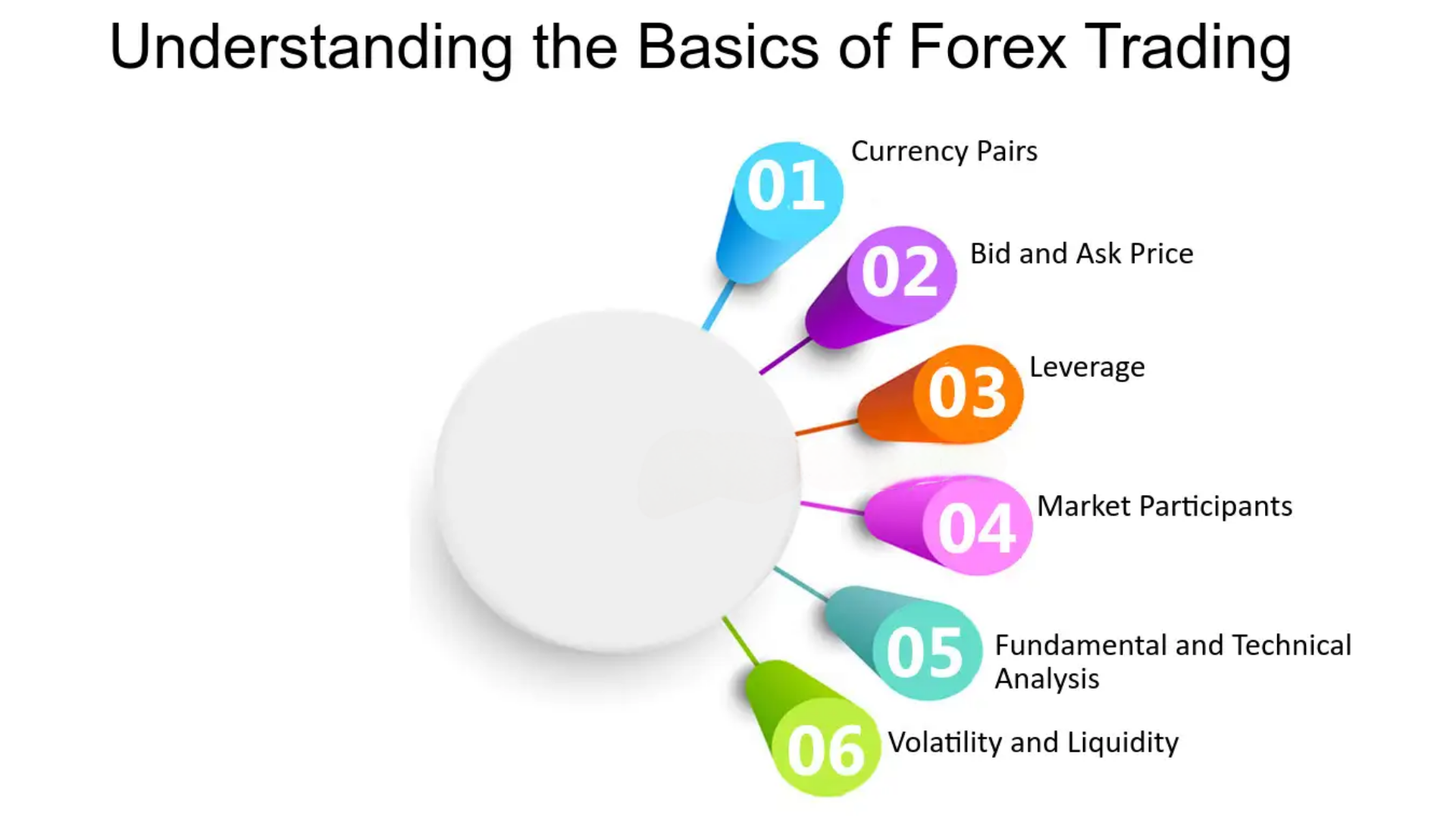
The forex market enables businesses, governments, and individual traders to buy, sell, and speculate on currency values. To succeed in forex trading, it’s essential to understand its foundational elements. So let’s break down the basics:
1. What is Forex?
Forex involves trading one currency for another. For example, when you trade the EUR/USD currency pair, you are buying euros while simultaneously selling US dollars. The forex market operates entirely online and is decentralized, meaning there is no central exchange—transactions occur across a network of banks, brokers, and traders.
2. Currency Pairs
In forex, currencies are always traded in pairs, such as GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar) or USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen). The first currency in the pair is the “base currency,” and the second is the “quote currency.” The price of the pair represents how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency. For instance, if GBP/USD is quoted at 1.3000, it means 1 British Pound equals 1.30 US Dollars.

Another example:
- GBP/USD = 1.12655
- This means one British Pound equals 1.12655 US Dollars.
- When you buyGBP/USD, you expect the Pound to appreciate against the Dollar.
- When you sellGBP/USD, you expect the Pound to depreciate against the Dollar.
3. Currency Abbreviations
Each currency is represented by a three-letter ISO code. Here are some of the most traded currencies:
- USD:US Dollar (“Dollar”)
- AUD:Australian Dollar (“Aussie”)
- NZD:New Zealand Dollar (“Kiwi”)
- EUR:Euro
- CAD:Canadian Dollar (“Loonie”)
- GBP:British Pound (“Pound”)
- JPY:Japanese Yen (“Yen”)
- CHF:Swiss Franc (“Swiss”)
4. Major, Minor, and Exotic Pairs
- Major Pairs:These pairs include the US dollar and are the most traded globally (e.g., EUR/USD, USD/JPY).
- Minor Pairs:These do not involve the US dollar but consist of other major currencies (e.g., EUR/GBP, AUD/NZD).
- Exotic Pairs:These combine a major currency with a less commonly traded currency, such as USD/TRY (US Dollar/Turkish Lira).
5. Market Hours
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, due to its decentralized nature. Trading sessions are divided into four major time zones:
- Sydney Session
- Tokyo Session
- London Session
- New York Session
These sessions overlap, providing traders with opportunities to trade at nearly any hour of the day.
6. Leverage and Margin
Forex brokers offer leverage, allowing traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. For example, a leverage ratio of 1:100 means that for every $1 you invest, you can control $100 in the market. While leverage can amplify profits, it also increases the potential for significant losses, so it must be used carefully.
7. Pips and Lots
- Pip:A pip is the smallest price movement in a currency pair. For most pairs, it is the fourth decimal place (e.g., a move from 1.2000 to 1.2001 equals one “1” pip).
- Lot Sizes:Forex trading positions are measured in lots:
- Standard Lot: 100,000 units of the base currency
- Mini Lot: 10,000 units
- Micro Lot: 1,000 units
- Nano Lot: 100 units
8. Bid, Ask, and Spread
- Bid Price:The price at which a trader can sell a currency pair.
- Ask Price:The price at which a trader can buy a currency pair.
- Spread:The difference between the bid and ask prices, representing the broker’s profit.
9. Types of Analysis in Forex Trading
To make informed trading decisions, traders rely on two primary types of analysis:
- Technical Analysis:Involves studying historical price charts and patterns to predict future movements basically using technical tools like support & resistance, trends, candlesticks, chart pattern etc.
- Fundamental Analysis:Focuses on economic indicators, geopolitical events, and market news to assess the strength of a currency.
10. Risk Management
Successful forex trading requires effective risk management. This includes using the appropriate lots sizing for your position, setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, diversifying trades, and using leverage responsibly. Understanding and managing risk is crucial to long-term success in the forex market.
By mastering these forex basics, traders will have the opportunity to build a solid foundation to navigate the complexities of the forex market effectively. Remember, continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a successful trader.
Forex Jargon Simplified
What Is a Pip?
A pip (percentage in point) is the smallest price movement in a currency pair. Most currencies are quoted to the fourth decimal place, where the fourth digit represents one pip. For example:
- If AUD/USD moves from 0.6751 to 0.6752, it has increased by 1 pip.
- Exceptions, like JPY pairs, are quoted to two decimal places (e.g., 146.20 to 146.21).
Lot Sizes
Trades are measured in lots:
- Standard Lot:100,000 units of the base currency.
- Mini Lot:10,000 units.
- Micro Lot:1,000 units.
- Nano Lot:100 units.
Bid, Ask, and Spread
- Bid Price:The price at which you sell a currency.
- Ask Price:The price at which you buy a currency.
- Spread:The difference between the bid and ask price, representing the broker’s profit.
The Role of Brokers and Leverage
Brokers
Retail traders require brokers to access the forex market. Brokers facilitate trades and offer platforms for analyzing the market, placing a position and managing them.
Leverage
Leverage allows you to control larger trade positions with a smaller deposit. For example, a leverage of 1:100 means you can control $100,000 with just $1,000. However, leverage is a double-edged sword; it amplifies both potential profits and losses.
Market Dynamics: Liquidity and Volatility
Liquidity
The forex market’s vast size ensures high liquidity, meaning traders can easily enter and exit positions without significantly impacting prices.
Volatility
- High Volatility:Rapid and large price swings, offering higher risk and reward.
- Low Volatility:Stable price movements, offering lower risk and reward.
Factors influencing volatility include:
- Economic data (e.g., GDP, inflation rates)
- Political events
- Central bank decisions
- Natural disasters
Analyzing the Forex Market
Technical Analysis
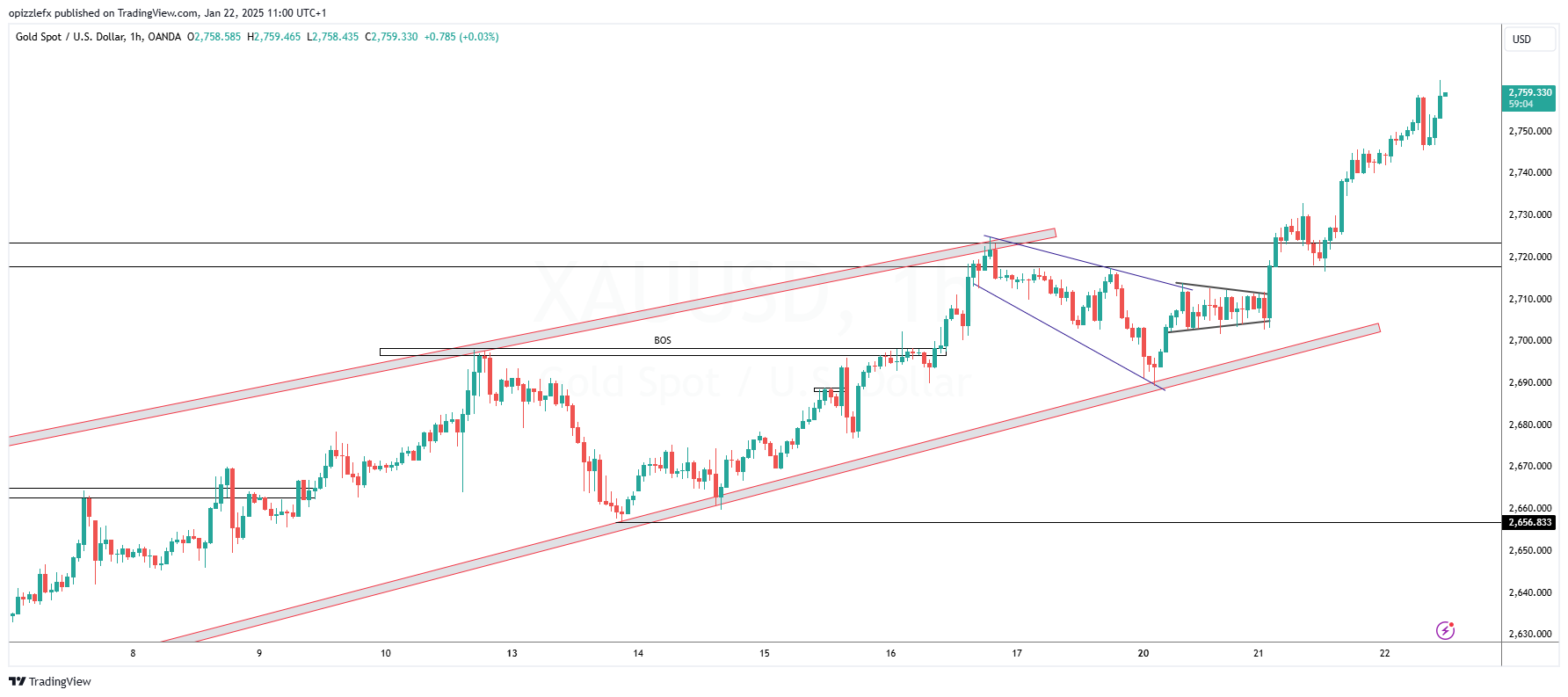
Technical analysis involves studying historical price data to predict future movements. Key tools include:
- Trend-lines: Identify uptrends or downtrends.
- Support and Resistance Levels:Highlight areas where prices tend to reverse.
- Chart Patterns:Recognize formations like head and shoulders or double tops.
Fundamental Analysis

Fundamental analysis examines economic indicators and geopolitical events to assess a currency’s value. Traders consider factors like:
- GDP growth
- Interest rates
- Employment data
- Political stability
Common Forex Trading Strategies
- Day Trading: Traders open and close positions within the same trading day to capitalize on short-term price movements.
- Swing Trading: Swing traders hold positions for several days to weeks, aiming to profit from medium-term trends.
- Scalping: Scalpers make multiple small trades within minutes or hours, targeting tiny price changes.
- Position Trading: This long-term strategy involves holding positions for weeks or months, focusing on major economic trends.
Tips for Beginners
- Start Small: Begin with a demo account to practice without risking real money.
- Focus on Major Pairs: They are less volatile and more liquid.
- Learn Risk Management: Use stop-loss orders and never risk more than 1-2% of your capital on a single trade.
- Stay Informed: Follow economic news and updates.
- Choose a Reputable Broker: Ensure they are regulated and offer competitive spreads. ( Broker Guide Here )
Conclusion
Forex trading offers immense opportunities for those willing to invest time and effort into learning the market. By understanding key concepts like currency pairs, pips, and leverage, and employing strategies like technical and fundamental analysis, you can develop the skills needed to succeed in this exciting field. Ready to dive deeper? Check out our free Forex Trading Beginner’s Guide linked below!
Don’t forget to hit the like button and share your thoughts in the comments. Stay tuned for more expert tips and tutorials on forex trading!
Important Links:
Become a member of OTC circle: Enroll Now
Join our telegram community channel: Join Now
About Me: Read more
Thanks sir for this. It’s helpful and simplified.
We’re glad you found our content useful. Thanks for your feedback